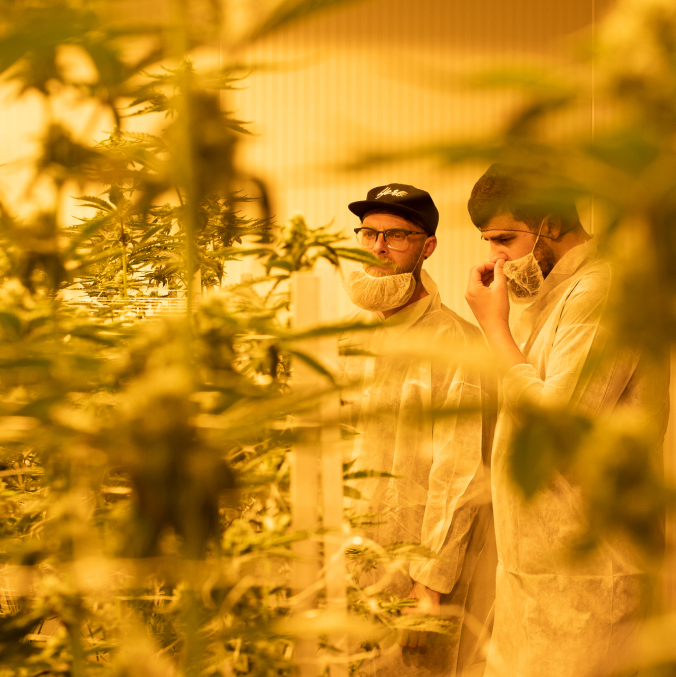
Your guide to understanding cannabis
Cannabis can be complex, but we’re here to simplify it. Whether you’re new to cannabis or looking to deepen your knowledge, this page covers everything from its history and benefits to responsible use. Explore the facts and insights you need to make informed choices.